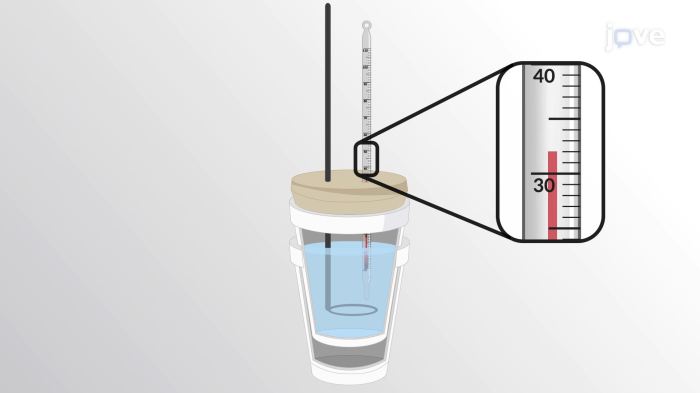
In a coffee cup calorimeter 50.0 ml, we delve into the fascinating world of calorimetry, where the measurement of heat transfer and energy changes takes center stage. Calorimetry finds applications in diverse fields, from chemistry and biology to engineering and materials science.
As we explore the principles, techniques, and applications of calorimetry, we gain insights into the intricate dance of energy within chemical reactions and physical processes.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with a thorough understanding of calorimetry, enabling you to navigate the intricacies of heat transfer and energy changes with confidence.
Introduction
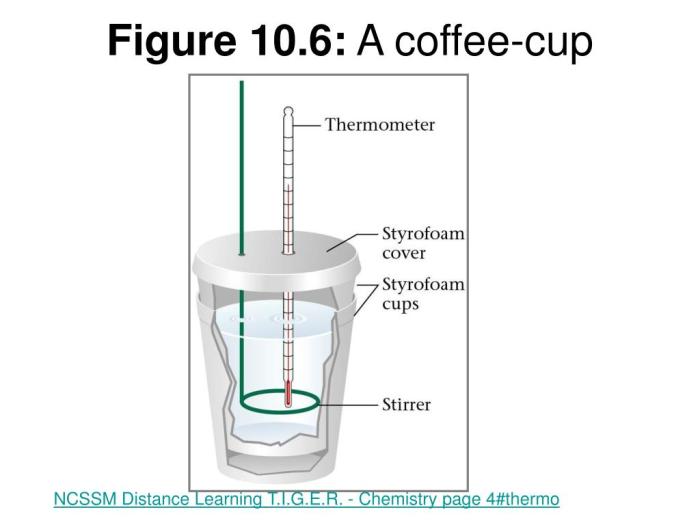
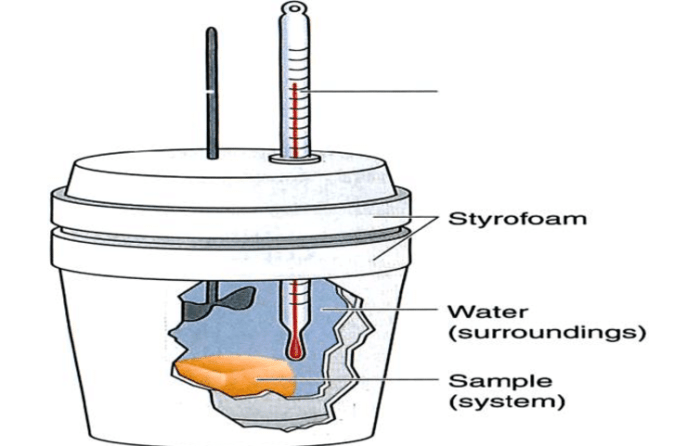
A coffee cup calorimeter is a simple device used to measure the heat released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. It consists of a foam or plastic cup filled with a known mass of water, and a thermometer to measure the change in temperature of the water.
Calorimetry is the study of heat transfer and its applications. It is an important tool in many fields, including chemistry, biology, and physics. Calorimetry can be used to measure the heat of a reaction, the specific heat of a substance, and the enthalpy of a reaction.
Importance of Calorimetry
- Chemistry:Calorimetry is used to study the thermodynamics of chemical reactions. By measuring the heat released or absorbed during a reaction, chemists can determine the enthalpy change of the reaction.
- Biology:Calorimetry is used to study the metabolism of cells and organisms. By measuring the heat produced by cells, biologists can determine the rate of metabolic reactions.
- Physics:Calorimetry is used to study the thermal properties of materials. By measuring the specific heat of a substance, physicists can determine the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the substance by one degree Celsius.
Experimental Setup: In A Coffee Cup Calorimeter 50.0 Ml
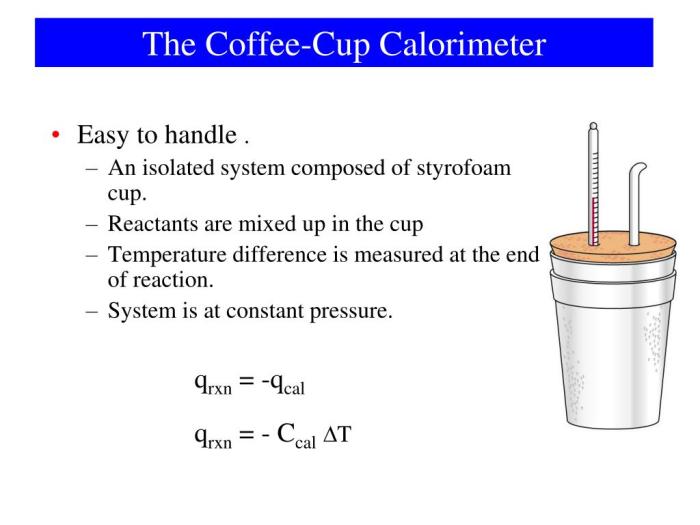
The experimental setup for a coffee cup calorimeter involves utilizing various materials and equipment to accurately measure the heat changes in chemical reactions or physical processes. The calorimeter is designed to minimize heat loss to the surroundings, allowing for precise determination of the heat involved in the reaction.
Materials
- Styrofoam cup: Acts as an insulating container for the reaction.
- Thermometer: Measures the temperature change of the solution.
- Stirrer: Ensures uniform mixing and temperature distribution.
- Reactants: The substances undergoing the chemical reaction or physical process.
- Water: Solvent for the reaction or to absorb the heat released/absorbed.
Procedure
- Place the Styrofoam cup inside a larger cup or container for added insulation.
- Fill the Styrofoam cup with a known mass of water (typically 50-100 mL).
- Measure the initial temperature of the water using the thermometer.
- Add the reactants to the water and stir to initiate the reaction or process.
- Continuously stir the solution and record the temperature at regular intervals until it stabilizes.
- Calculate the heat change using the formula: Q = mCpΔT, where Q is the heat change, m is the mass of water, C pis the specific heat capacity of water (4.184 J/g°C), and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Diagram
[Insert a diagram illustrating the experimental setup, including the Styrofoam cup, thermometer, stirrer, reactants, and water.]
Data Collection and Analysis
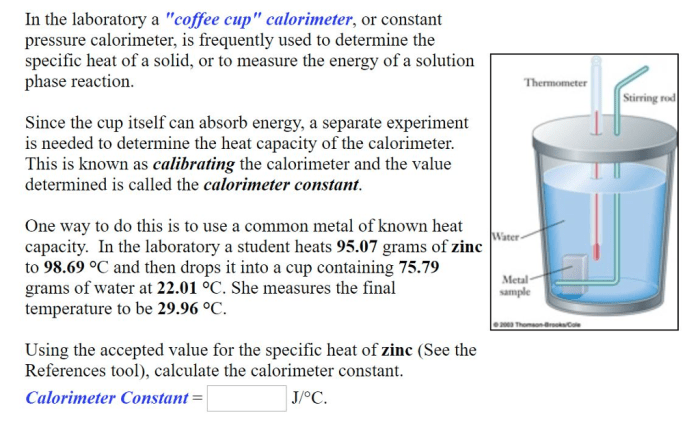
In a coffee cup calorimeter, temperature changes are measured using a thermometer. The thermometer is inserted into the solution, and the temperature is recorded at regular intervals. The temperature change is calculated by subtracting the initial temperature from the final temperature.
The heat capacity of the system is determined by dividing the heat absorbed or released by the temperature change. The heat absorbed or released is calculated by multiplying the mass of the solution by the specific heat capacity of the solution and the temperature change.
Sources of Error
There are several sources of error that can affect the accuracy of the heat capacity measurement. These include:
- Heat loss to the surroundings
- Evaporation of the solution
- Errors in measuring the temperature
- Errors in measuring the mass of the solution
To minimize these errors, the following precautions should be taken:
- The calorimeter should be insulated to minimize heat loss to the surroundings.
- The solution should be covered to minimize evaporation.
- A calibrated thermometer should be used to measure the temperature.
- The mass of the solution should be measured accurately.
Applications
Coffee cup calorimeters find diverse applications in various fields. They are particularly useful for measuring heat changes in chemical reactions, determining specific heats of substances, and understanding energy transformations.
One of the primary applications of coffee cup calorimeters is in chemistry. They are commonly used to determine the enthalpy changes associated with chemical reactions. By measuring the temperature change of the calorimeter and its contents, it is possible to calculate the heat released or absorbed during the reaction.
This information is crucial for understanding the thermodynamics of chemical reactions and predicting their feasibility.
Educational Use
Coffee cup calorimeters are also widely employed in educational settings. They provide a simple and cost-effective method for students to investigate calorimetry and energy transfer. Students can perform experiments to determine the specific heat of various substances, study the effects of different variables on heat transfer, and explore the principles of thermodynamics.
Industrial Applications, In a coffee cup calorimeter 50.0 ml
In industry, coffee cup calorimeters are used for quality control and product development. For instance, they can be employed to measure the heat capacity of food products, ensuring they meet specific quality standards. Additionally, they can be used to optimize manufacturing processes by monitoring heat transfer and energy efficiency.
Despite their versatility, coffee cup calorimeters have certain limitations. Their accuracy is limited by heat losses to the surroundings and the sensitivity of the temperature probe. Additionally, they are not suitable for reactions that produce large amounts of heat or involve volatile or corrosive substances.
Despite these limitations, coffee cup calorimeters remain a valuable tool for a wide range of applications. Their simplicity, low cost, and ease of use make them an accessible option for both educational and industrial purposes.
Common Queries
What is the purpose of a coffee cup calorimeter?
A coffee cup calorimeter is a simple and inexpensive device used to measure heat transfer and energy changes in chemical reactions and physical processes.
How does a coffee cup calorimeter work?
A coffee cup calorimeter works by measuring the temperature change of a known mass of water when a chemical reaction or physical process occurs in the water.
What are the limitations of a coffee cup calorimeter?
Coffee cup calorimeters are limited in accuracy and precision compared to more sophisticated calorimeters, and they cannot be used to measure heat transfer in reactions that produce gases or involve large temperature changes.