Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of geometry as we delve into the intricacies of its foundations. The Foundations of Geometry Answer Key serves as an indispensable guide, illuminating the fundamental principles and theorems that underpin this fascinating field.
Within this comprehensive resource, you’ll unravel the concepts of points, lines, and planes, exploring their relationships and the angles they form. Geometric figures, from triangles to circles, will be dissected, revealing their properties and measurements. The art of geometric transformations and symmetry will be unveiled, showcasing their applications in real-world scenarios.
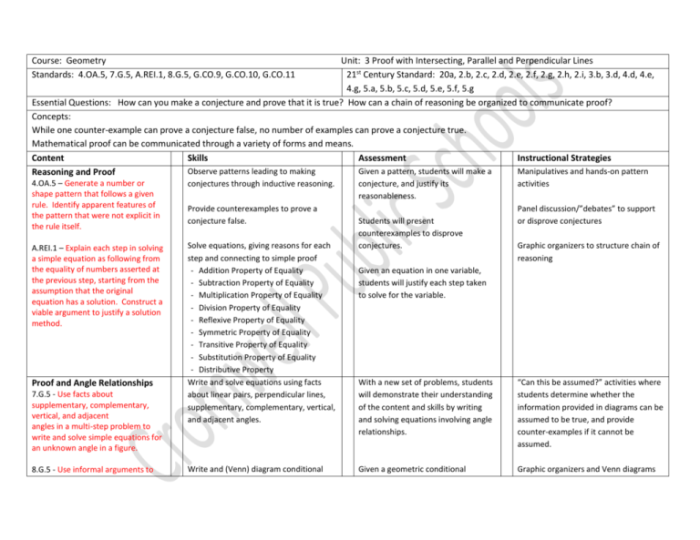
1. Basic Concepts
Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of space and the relationships between points, lines, planes, and shapes.
The fundamental principles of geometry include the following:
- Points are the basic building blocks of geometry. They have no size or shape and are represented by a single dot.
- Lines are one-dimensional objects that extend in two directions. They are represented by a straight line.
- Planes are two-dimensional objects that extend in all directions. They are represented by a flat surface.
- Angles are formed when two lines or planes intersect. They are measured in degrees.
- Shapes are two-dimensional or three-dimensional objects that are bounded by lines or planes.
2. Geometric Figures
There are many different types of geometric figures, including triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and spheres.
Triangles are three-sided figures. They are classified by the length of their sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral) and the measure of their angles (acute, right, obtuse).
Quadrilaterals are four-sided figures. They are classified by the length of their sides (trapezoid, parallelogram, rectangle, square) and the measure of their angles (convex, concave).
Circles are two-dimensional figures that are defined by a center point and a radius. They are characterized by their circumference and area.
Spheres are three-dimensional figures that are defined by a center point and a radius. They are characterized by their surface area and volume.
3. Measurement and Calculation
The measurement of angles, distances, and areas is essential in geometry.
Angles are measured in degrees using a protractor. Distances are measured in units such as inches, centimeters, or meters using a ruler or tape measure. Areas are measured in square units such as square inches, square centimeters, or square meters using a formula.
Geometric formulas and theorems can be used to solve a variety of problems. For example, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
4. Transformations and Symmetry
Geometric transformations are operations that move, rotate, or reflect figures.
The most common geometric transformations are:
- Translation: moving a figure from one place to another without changing its size or shape.
- Rotation: turning a figure around a fixed point.
- Reflection: flipping a figure over a line.
Symmetry is the property of a figure that looks the same when it is transformed.
There are two types of symmetry:
- Line symmetry: a figure has line symmetry if it looks the same when it is reflected over a line.
- Rotational symmetry: a figure has rotational symmetry if it looks the same when it is rotated around a point.
5. Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate geometry is a branch of geometry that uses algebra to represent and analyze geometric figures.
The Cartesian coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system that uses two perpendicular axes, the x-axis and the y-axis, to locate points in a plane.
Coordinate geometry can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as finding the distance between two points or the area of a triangle.
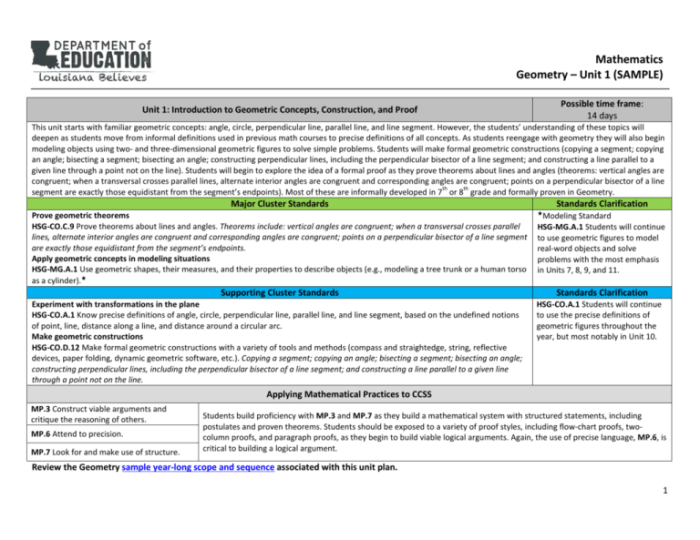
6. Proofs and Theorems, Foundations of geometry answer key
A geometric proof is a logical argument that establishes the truth of a geometric statement.
There are two main types of geometric proofs:
- Deductive proofs: these proofs start with a set of axioms (statements that are assumed to be true) and use logical reasoning to derive new statements.
- Synthetic proofs: these proofs start with a given figure and use geometric constructions to derive new properties of the figure.
Geometric theorems are statements that have been proven to be true.
Some of the most famous geometric theorems include the Pythagorean theorem, the triangle inequality theorem, and the circle area theorem.
FAQ Overview: Foundations Of Geometry Answer Key
What is the significance of geometric proofs?
Geometric proofs establish the validity of geometric statements through logical reasoning, providing a solid foundation for mathematical knowledge.
How is coordinate geometry used in real-world applications?
Coordinate geometry finds applications in fields such as navigation, computer graphics, and architecture, enabling the precise representation and manipulation of geometric shapes.
What are the key concepts of geometric transformations?
Geometric transformations involve moving or altering geometric figures without changing their inherent properties, such as translations, rotations, and reflections.