Chapter 6 general anatomy and physiology milady – Chapter 6: General Anatomy and Physiology in Milady’s textbook provides a comprehensive overview of the human body, its structure, and its functions. This chapter serves as a foundational pillar for understanding the intricate workings of the human organism, laying the groundwork for further exploration of specific systems and their contributions to overall health and well-being.
The chapter delves into the integumentary system, the skeletal system, the muscular system, the nervous system, the endocrine system, and more, providing a holistic perspective on the human body and its remarkable complexity.
Introduction
Chapter 6 of Milady’s General Anatomy and Physiology textbook provides a comprehensive overview of the human body’s structural and functional components. This chapter serves as a foundation for understanding the complex interplay between different systems and organs, enabling readers to appreciate the intricate mechanisms that govern human life.
Integumentary System

The integumentary system, composed of the skin, hair, and nails, acts as a protective barrier against external elements and plays a crucial role in thermoregulation and sensation.
Structure and Functions of the Skin
- Epidermis:The outermost layer, providing a waterproof barrier and containing pigment-producing cells.
- Dermis:The middle layer, composed of connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
- Hypodermis:The innermost layer, consisting of fat cells and providing insulation and cushioning.
Structure and Functions of Hair and Nails
Hair and nails are appendages of the skin that serve specialized functions.
- Hair:Protects against UV radiation, provides insulation, and enhances sensory perception.
- Nails:Protect the tips of fingers and toes, facilitate gripping and manipulation, and provide a platform for nail art.
Skeletal System
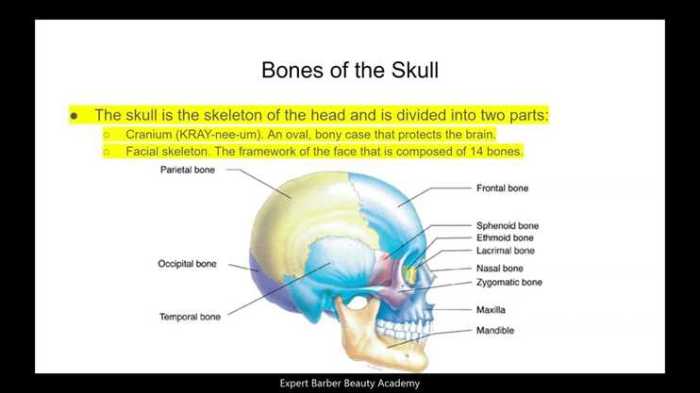
The skeletal system provides support, protection, and facilitates movement. It comprises various types of bones with unique structures and functions.
Types of Bones, Chapter 6 general anatomy and physiology milady
- Long bones:Long and cylindrical, found in the limbs and providing support and movement.
- Short bones:Cube-shaped, found in the wrist and ankle, and providing stability.
- Flat bones:Thin and plate-like, forming the skull and ribs, and providing protection and attachment sites for muscles.
- Irregular bones:Complex shapes, found in the face and vertebrae, and providing unique functions.
Structure and Organization of the Skeletal System
Bones are connected by joints, which allow for movement, and ligaments, which provide stability.
- Joints:Types include ball-and-socket, hinge, pivot, and saddle, each enabling specific ranges of motion.
- Ligaments:Tough, fibrous bands of connective tissue that connect bones and limit excessive movement.
Muscular System

The muscular system, composed of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, generates movement and maintains posture.
Structure and Function of Muscles
- Skeletal muscles:Voluntary, striated muscles attached to bones, enabling conscious movement.
- Smooth muscles:Involuntary, non-striated muscles found in organs and blood vessels, regulating involuntary functions.
- Cardiac muscles:Involuntary, striated muscles found in the heart, responsible for pumping blood.
Types of Muscle Contractions
- Isotonic contractions:Muscles shorten, causing movement.
- Isometric contractions:Muscles generate force without changing length, maintaining posture.
FAQ Resource: Chapter 6 General Anatomy And Physiology Milady
What is the significance of the integumentary system?
The integumentary system plays a crucial role in protection, thermoregulation, and sensation, acting as a barrier against external threats and maintaining optimal body temperature.
How does the skeletal system contribute to movement?
The skeletal system provides support and framework for the body, facilitates movement through joints and ligaments, and protects vital organs.
What is the primary function of the muscular system?
The muscular system is responsible for movement, posture, and heat production, enabling a wide range of bodily functions and maintaining overall mobility.