The graph depicts the market for loanable funds, a fascinating and dynamic aspect of the financial system. This market plays a pivotal role in facilitating the flow of funds between savers and borrowers, thereby influencing economic growth and stability.
Factors such as time preference, risk aversion, and expectations shape the supply and demand for loanable funds, while interest rates serve as a crucial mechanism for equilibrating the market.
Market for Loanable Funds
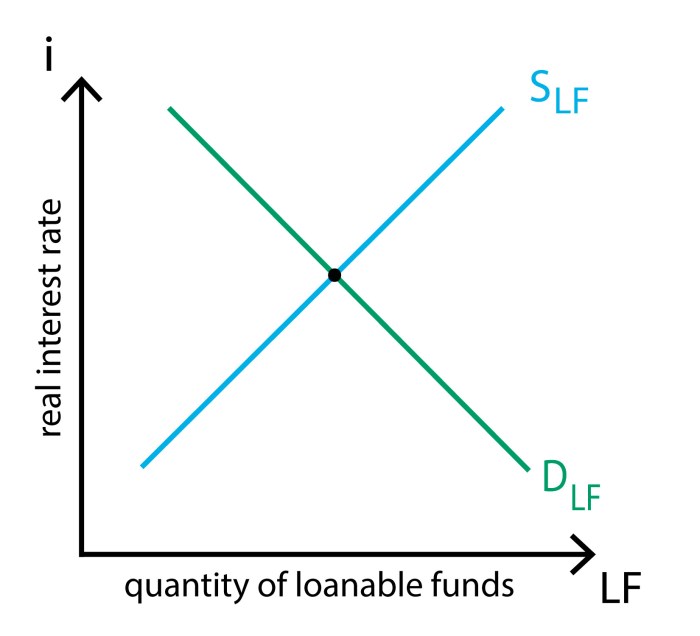
The market for loanable funds is a financial market where individuals, businesses, and governments borrow and lend money. It plays a crucial role in the allocation of capital and the determination of interest rates in an economy.
Factors Affecting Supply and Demand
The supply of loanable funds comes from savings, while the demand comes from investment and government borrowing. Factors that affect the supply include income, wealth, and the expected rate of return on investments. Factors that affect the demand include the cost of capital, the expected return on investments, and government spending.
Role of Interest Rates
Interest rates are the price of loanable funds. They play a central role in the market for loanable funds. Higher interest rates encourage saving and discourage borrowing, while lower interest rates discourage saving and encourage borrowing. This helps to balance the supply and demand for loanable funds.
Equilibrium in the Market for Loanable Funds: The Graph Depicts The Market For Loanable Funds
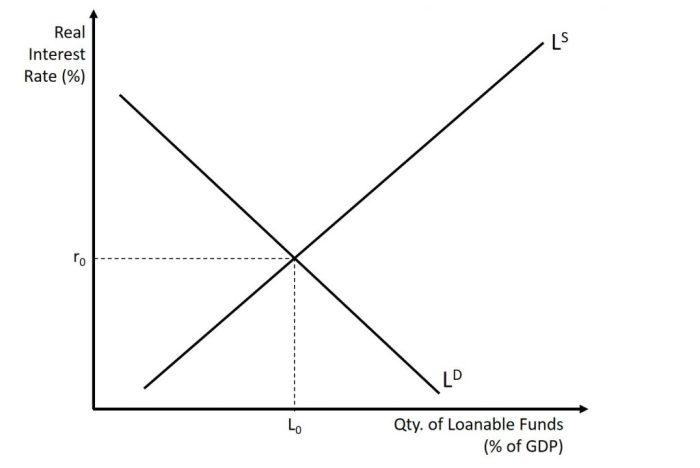
Equilibrium in the market for loanable funds occurs when the quantity of loanable funds supplied equals the quantity demanded. At this point, the interest rate is called the equilibrium interest rate.
Factors Shifting Equilibrium
Factors that can shift the equilibrium in the market for loanable funds include changes in savings, investment, government spending, and the expected rate of return on investments.
Impact of Changes in Equilibrium, The graph depicts the market for loanable funds
Changes in the equilibrium interest rate can have a significant impact on the economy. For example, a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate can lead to increased investment and economic growth, while an increase in the equilibrium interest rate can lead to decreased investment and economic slowdown.
Policy Implications of the Market for Loanable Funds
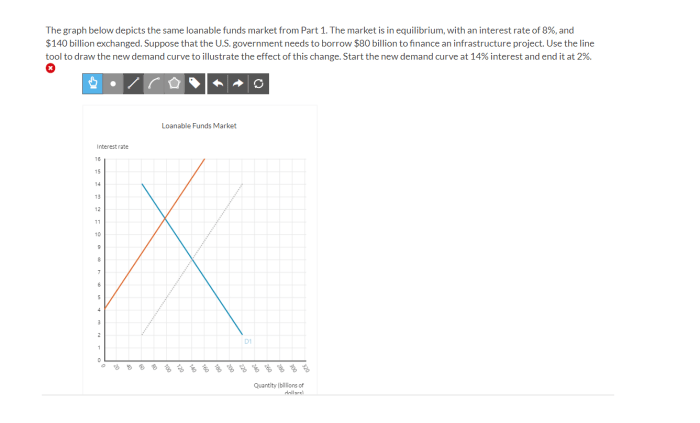
The market for loanable funds has important implications for monetary policy. Monetary policy is the set of tools used by central banks to control the supply of money and interest rates in an economy.
Monetary Policy and the Market for Loanable Funds
Central banks can use monetary policy to influence the market for loanable funds. For example, they can increase the money supply to lower interest rates and encourage borrowing, or they can decrease the money supply to raise interest rates and discourage borrowing.
Risks and Benefits of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy can be a powerful tool for managing the economy, but it also carries risks. For example, excessive monetary expansion can lead to inflation, while excessive monetary contraction can lead to recession.
FAQ Insights
What is the market for loanable funds?
The market for loanable funds is a financial marketplace where individuals and institutions lend and borrow money for a specified period.
How do interest rates affect the market for loanable funds?
Interest rates influence the supply and demand for loanable funds. Higher interest rates encourage saving and discourage borrowing, while lower interest rates have the opposite effect.
What is the role of monetary policy in the market for loanable funds?
Monetary policy can be used to influence the supply and demand for loanable funds by adjusting interest rates. This can help stabilize the economy and promote economic growth.