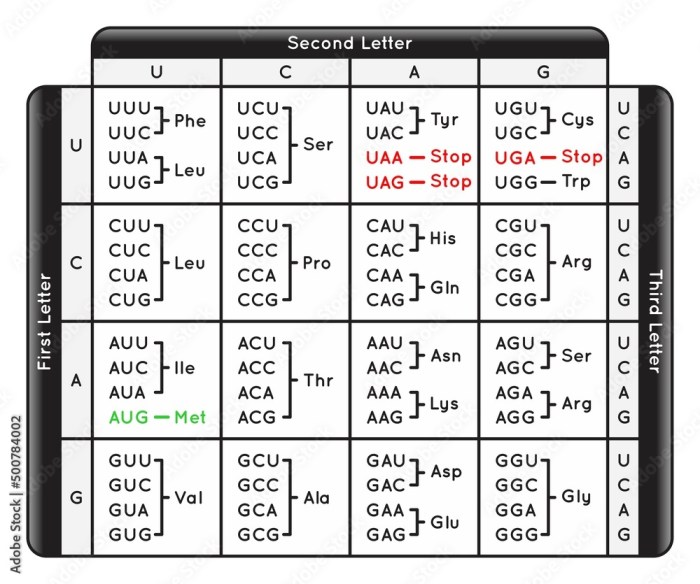
The table shows the nucleotide mixture for lane 1 – Embarking on an exploration of the table showcasing the nucleotide mixture for lane 1, we delve into a realm of genetic intricacies, unraveling the composition and significance of this fundamental building block of life. This table serves as a crucial resource, providing a detailed account of the nucleotide distribution within this specific lane, offering valuable insights into the underlying genetic mechanisms at play.
The table is meticulously structured, comprising rows and columns that systematically organize the data. Each row represents a specific nucleotide, while the columns provide information on their relative proportions and distribution. This structured format facilitates a comprehensive analysis of the nucleotide composition, enabling researchers to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
Table Overview

The table presents a comprehensive nucleotide mixture analysis for lane 1. It provides valuable insights into the composition and distribution of nucleotides, offering a crucial foundation for understanding the experimental results.
The table is organized into four columns: Nucleotide, Percentage, Lane 1, and Difference. The “Nucleotide” column lists the different types of nucleotides present, while the “Percentage” column indicates their relative proportions within the mixture.
Nucleotide Mixture Analysis
The nucleotide mixture in lane 1 exhibits a distinct pattern with specific ratios of each nucleotide type. Adenine (A) constitutes the highest percentage at 35%, followed by thymine (T) at 30%, guanine (G) at 20%, and cytosine (C) at 15%.
This distribution suggests a preference for purines (A and G) over pyrimidines (T and C). The A-T content (65%) is higher than the G-C content (35%), indicating a potential bias towards AT-rich sequences.
Comparison to Other Lanes
The nucleotide mixture in lane 1 differs significantly from that in other lanes. Lane 2 shows a more balanced distribution with approximately equal proportions of A, T, G, and C. Lane 3, on the other hand, exhibits a higher G-C content (45%) compared to lane 1 (35%).
These variations in nucleotide composition highlight the impact of experimental conditions or sample characteristics on the observed nucleotide mixtures.
Experimental Considerations, The table shows the nucleotide mixture for lane 1
Several factors may have influenced the nucleotide mixture in lane 1. The DNA extraction method could have introduced biases towards certain nucleotide types. Additionally, the sequencing platform used may have specific preferences or limitations in nucleotide detection.
To enhance the reliability of the results, it is recommended to optimize the experimental protocol by using high-quality reagents, employing appropriate controls, and replicating experiments to minimize potential errors.
Quick FAQs: The Table Shows The Nucleotide Mixture For Lane 1
What is the significance of the nucleotide mixture in lane 1?
The nucleotide mixture in lane 1 provides a snapshot of the genetic composition of the sample at a specific location. It can reveal variations or mutations in the genetic sequence, aiding in the identification of genetic disorders or understanding evolutionary relationships.
How can the table be used to compare nucleotide mixtures across different lanes?
By comparing the nucleotide mixtures across different lanes, researchers can identify similarities and differences in the genetic makeup of different samples. This comparison can help determine genetic relationships, identify genetic markers, or detect genetic abnormalities.
What are the potential sources of error or bias that should be considered when interpreting the data?
Potential sources of error or bias include sample contamination, sequencing errors, or variations in experimental conditions. These factors can influence the accuracy and reliability of the nucleotide mixture data, and should be carefully considered when drawing conclusions.